

Then, since the lithium ion has one less electron, remove Aug 10, 2023 To simplify the problem let us consider a d 2 ion in an octahedral ligand field first (Fig. Nickel atoms have 28 electrons and the shell structure is 2.By finely tuning the oxidation states of metal single atoms, their electronic configurations were modulated, resulting in more … Aug 2, 2016.According to Crystal Field Theory, CNX− C N X − is a strong field ligand that causes pairing of electrons i.Herein, hierarchical gallium (Ga)-doped NiFe2O4 (Ga-NiFe2O4) nanosheet arrays grown on nickel foam (NF) is successfully fabricated by a straightforward … Jun 27, 2019.This type of configuration is quite comparable to that of the noble-gas atoms. Know the nickel atomic number, Chemical Properties of Nickel, Atomic Mass, and 2− Geometry at BYJU'S. The first example occurs in the case of the lanthanoids (elements having atomic numbers between 57 and 71). In general, the electronic configuration of outer orbitals of these elements is (n-1) d 1-10 n s 1-2. The energy level, "n", can be determined based on the periodic table, simply by looking at the row number in which the element is in. Each of the three connected square which represents the 2p orbitals are filled with one arrow respectively with the addition of > Position in the Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration(d-block) > The electronic configuration of Cu^2 + Question. prepared nickel ferrite using pulsed wire discharge (PWD) method and observed saturation magnetization of 33 emu g −1 and particle size of 45 nm. Again, the nickel atom donates two electrons in the 4s orbital and an electron in the 3d orbital to convert nickel ion(Ni 3+). So skip, manganese, skip iron, skip cobalt, skip nickel, and then you land on copper, where the next group of exceptions can exist. The empty 4s and three 4p orbitals undergo sp3 hybridization and form bonds with CO ligands to give Ni (CO)4. The cobalt atom donates two electrons in the 4s orbital and an electron in the 3d orbital to convert a cobalt ion (Co 3+ ). To write the electronic structure for Fe 3 +: Fe: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 6 4s 2 Fe 3 +: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 5 The 4s electrons are lost first followed by one of the 3d electrons. 202104349 The distribution of electrons into orbitals of an atom is called its electronic configuration.
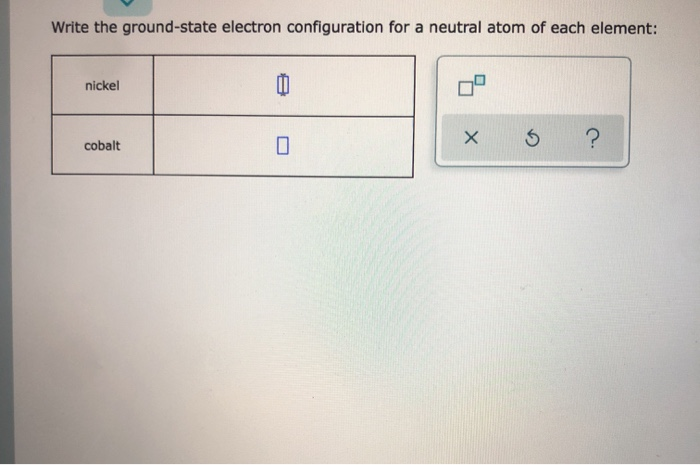
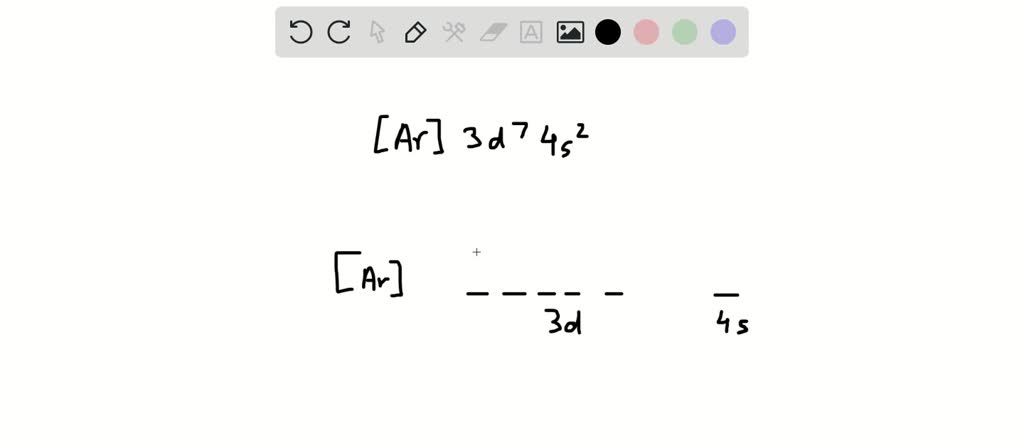
Nickel (Ni) electron configuration Electronic configuration table Electronic Configuration: With the help of atomic number of any particular element existing in the periodic table, the electron configuration can be written easily. The equation is: 1s> Position in the Periodic Table and Electronic Configuration(d-block) > The electronic configuration of Cu^2 + Question. The empty orbitals (one 3 d, one 4 s and two 4 p orbitals) undergo d s p 2 hybridization to make bonds with four C N − ligands which result in The magnetic properties of a substance can be determined by examining its electron configuration: If it has unpaired electrons, then the substance is paramagnetic and if all electrons are paired, the substance is then diamagnetic. And for the excited state, it is 1s 2 2s 1 2p 2. In the case of first row transition metals, the electron configuration would simply be 4s x 3d x. The general electronic configuration of d-block element is (n−1)d1−10ns1−2, where n is the outer most shell. (ii) One isotope of cobalt is used in the treatment of cancer.Electronic configuration of nickel. (i) One isotope of uranium is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors. Isobars are atoms having the same mass number, but different atomic numbers i.e., isobars are atoms of different elements having the same mass number. They are protium, deuterium, and tritium. For example, hydrogen has three isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element having the same atomic number, but different mass numbers. So, the mass number of boron is 5 + 6 = 11. For example, the atom of boron has 5 protons and 6 neutrons. The mass number of an element is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons present in the atom of that element. Thus, the atomic number of nitrogen is 7. For example, nitrogen has 7 protons in its atom. The atomic number of an element is the total number of protons present in the atom of that element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
